Transport of Fatty Acids Occurs From the
This reaction occurs in cytoplasm and is ATP and Mg 2. Triglycerols are degraded to fatty acids and glycerol in the adipose tissue and transported to other tissues.
Fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the cytoplasm of these tissues.

. 81 Placental proteins with greater affinity for DHA and ARA than for other fatty acids have been identified and their expression is increased in the placenta of women with. After a period of prolonged fasting starving the brain changes its fuel requirements and starts to use ketones and spares protein. There are still ongoing debates regarding the mechanisms by which free FAs are transported across cell membranes.
The enzyme contains biotin and adds a CO2 resulting in a carboxyl group to the methyl end of acetyl CoA. Transport into the mitochondrial matrix. The absorption of long chain fatty acids occurs both by passive diffusion and by facilitated transport also known as facilitated diffusion by specific protein carriers.
Shuttles fatty acids from the cytosol into the mitochondria. These data strongly suggest that fatty acid transfer from I-FABP to membranes occurs by direct collisional interaction of the protein with the phospholipid bilayer. Transport of acetyl coA into mitochondria.
On the one hand due to the lipophilic nature of FAs it has been proposed that they may be passively transported through the lipid bilayer by flip-flop diffusion. Too rapid transport of fatty acids from the blood to the intestine. Fatty Acid Transport into.
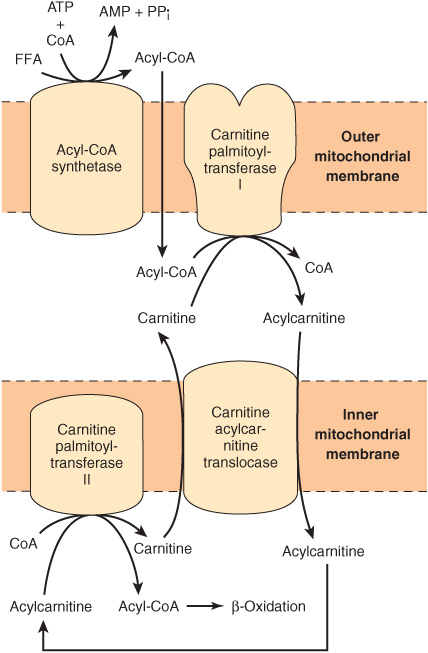
The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to fatty acids and a specialized carnitine carrier system operates to transport activated fatty acids from cytosol to mitochondria. This reaction is catalyzed by carnitine acyltransferase I. R-COOH CoASH ATP R-CO-SCoA AMP PP i.
Transport of Fatty Acids to the Epidermis. The acyl group is transferred from the sulfur atom of CoA to the hydroxyl group of carnitine to form acyl carnitine. This step is heavily regulated by the energy status of the cell.
Drinking more than 8 glasses of water in one day. Liver adipose fat central nervous system. Small 12 carbons fatty acids diffuse freely across mitochondrial membranes.
Transport of fatty acids by glycerides. The transport of fatty acyl-CoA across the outer mitochondrial membrane occurs by carnitinepalmitoyltransferase I CPT I. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion.
Fatty acid transport proteins FATPs are an evolutionary conserved family of integral membrane proteins found at the plasma membrane and on internal membranes. Blood small intestine 3. The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to fatty acids and a specialized carnitine carrier system operates to transport activated fatty acids from cytosol to mitochondria.
We conclude that cytoplasmic proteins like FABP promote the intracellular transport of fatty acids by enhancing their diffusive flux. PP i H 2 O -- 2 P i. Fatty acyl-carnitine is carried across the inner mitochondrial.
Too rapid transport of fatty acids from the intestine into the lymph. FATPs facilitate the unidirectional uptake andor intracellular activation of unesterified long-chain and very long-chain fatty acids into a variety of lipid-metabolizing cells and tissues. Acyl carnitine is shuttled inside by a translocase.
Fatty acid Synthesis Mechanism A. Skeletal muscle cells small intestine 4. Once activated the acyl CoA is transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
The first committed step of fatty acid biosynthesis is catalyzed by Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Urinary tract antigen 2. A type of transport of a solute across a membrane up its concentration gradient using protein carriers driven by the expenditure of chemical energy is known as A.
Fatty acids are activated and transported into the mitochondria. Placental uptake of fatty acids from the maternal plasma and transport across the placenta involves fatty acid transport and binding proteins with mechanisms for release of fatty acids to the fetal plasma. From the choices below one possible cause of localized fluid accumulation in the tissues is 1.
How are fatty acids transported into the cell. Damage to the lymph vessels such that they do not take up Questions 1. Fatty acids are activated by fatty acyl CoA synthetase.
Absorption of long chain fatty acids. The acyl-carnitine is transported across the membrane to mitochondrial matrix by a specific carrier protein Translocase. Transport of fatty acyl coA into mitochondria.
Lipoprotein lipase isolated from plasma adipose. Larger fatty acids most free fatty acids are transported via acyl-carnitinecarnitine transporter. An alternative path is to transport malate across the inner membrane and convert it to oxaloacetate.
From the choices below one possible cause of localized fluid accumulation in the tissues is 1. Fatty acids are transported to other tissues for fuel through the blood. Fatty acids stored as triglycerides in an organism are a concentrated source of energy because they contain little oxygen and are anhydrousThe energy yield from a gram of fatty acids is approximately 9 kcal 37 kJ much higher than the 4 kcal 17 kJ for carbohydrates because oxidation of a gram of fatty acids which contains relatively few oxygen atoms releases the.
This enzyme simultaneously converts fatty acylcarnitine. The reaction occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the outer. Small intestine lymphatic system 2.
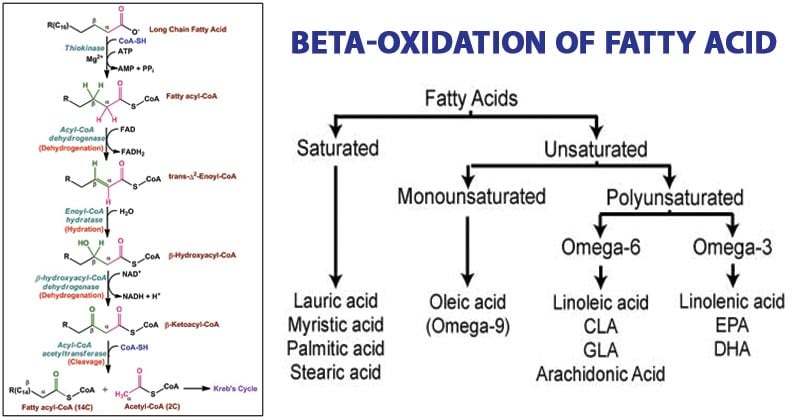
Activation of fatty acid. Utilization of Fatty Acids as Fuel. B oxidation of fatty acids occurs in mitochondria.
Malonyl-CoA levels rise during the synthesis of fatty acids and function to inhibit mitochondrial beta-oxidation at. It occur in four stages. Tissue and myocardium 215 216 218 appears to be identical to clearing factor.
The inner mitochondrial membrane doesnt permit fatty acids to pass through it. The subsequent hydrolysis of PPi draws the reaction in the forward direction maintaining a low cytosolic free fatty acid concentration. We suggest that facilitation is not specific for a particular cell type but occurs in a variety of cells that transport fatty acids and may contain different types of.
Fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon acetylCoA units and fed into the citric acid cycle. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism. First observed after injection of heparin into lipemic animals I 2 180 363.
Transport of fatty acids occurs from the into the 1. Activated long-chain fatty acids are transported across the membrane by conjugating them to carnitine a zwitter-ionic alcohol. In contrast the characteristics of fatty acid transfer from L-FABP are consistent with an aqueous diffusion-mediated process.
Once activated the acyl CoA is transported into the mitochondrial matrix. This occurs via a series of similar steps. Acyl group of acyl CoA is transferred to carnitine catalyzed by carnitine acyltransferase I CAT-I present on the outer surface of inner mitochondrial membrane.
Passive diffusion occurs via a flip-flop mechanism and affects protonated and thus uncharged fatty acids. Fatty acid is converted to fatty acyl CoA by thiokinase or fattyacyl CoA synthetase. Too rapid transport of fatty acids from the intestine into the lymph.
Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Ketogenesis Basicmedical Key

L Carnitine Linus Pauling Medical Therapy Mitochondrial

Pin On Https Drawittoknowit Com

Digestion And Absorption Of Lipids Human Nutrition Deprecated Human Nutrition Digestion Biochemistry Notes

Electron Transport Chains Are The Last Step Of Cellular Respiration Biology Lessons Electron Transport Chain Biochemistry

Aerobic Respiration Occurs In 3 Major Stages Online College College Study College Quotes

Fatty Acids Transport And Regeneration

Activation And Transportation Of Fatty Acids To The Mitochondria Via The Carnitine Shuttle With Animation Animations Pharmaxchange Info

Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Via Beta Oxidation Biochemistry Notes Pharmaxchange Info









Comments
Post a Comment